39 dosage calculations with labels
Drug Dosage Calculations | How-to-guide - KnowledgeDose The available stock is 2000 units/ml. The pharmacist has asked the pre-registration pharmacist to also state how many mls of colecalciferol Mr X should take on the dispensing label. What is the correct dosage on the label? Take 800 units (0.4ml) once daily Take 800 units (0.8ml) once daily Take 800 units (0.6ml) once daily 4 Gastroenteritis Nursing Care Plans - Nurseslabs Mar 18, 2022 · Hospitalization may be needed for clients who experience severe dehydration as a result of the vomiting and diarrhea. This care plan for Gastroenteritis focuses on the initial management in a non-acute care setting. Here are four (4) nursing care plans (NCP) for Gastroenteritis:
How to Read a Medication Label Nursing Quiz - Registered Nurse RN A. 7 doses. B. 5 doses. C. 20 doses. D. 12 doses. The answer is C (20 doses). The total volume amount after reconstitution (meaning once the nurse has mixed the medication) is 100 mL. The label tells us that in 5 mL of this medication there are 350 mg. The patient needs to take 350 mg twice a day.

Dosage calculations with labels
Lecture 3: Reading Medication Labels and Basic Dosage Calculations Every tenth of a cc(mL)is marked on the syringe, and every half cc(mL) is labeled; this means that any dosage we plan to measure using a 3 cc syringe should be rounded to the nearest tenth. Dosages between 1-3 mLshould always be measured in a 3 cc syringe. PDF Dosage Calculations Syllabus(1)new - Odessa College Chapter 6: Oral medication labels and dosage calculations (CO #1-5) The learner will: 1. Identify scored tablets, unscored tablets, and capsules. 2. Read drug labels to identify trade and generic names. 3. Locate dosage strengths and calculate average dosages. 4. Measure oral solutions using a medicine cup. Chapter 7: Safe medication administration Dosage Calculator - How to Calculate Dosage? Let's say the appropriate dosage of the active substance is 2 mg/kg of body weight. Weigh yourself. Let's assume you weigh 80 kg. Multiply these two values to get the dose of medication in mg: 2 * 80 = 160 mg. You need to take 160 mg of active substance. What if your medication is liquid? Type the concentration into the proper box.
Dosage calculations with labels. LibGuides: Clinical Calculations: Module 6: Divided Doses and ... The dosage strength of the reconstituted medication will be specified on the label. The dosage strength of the reconstituted medication is the strength the nurse will use in calculating the amount of medication to give the client according to the healthcare provider's prescription. ATI Dosage Calculations Final Exam 1 - Version 1 KEY Name - StuDocu Practice ATI questions for the final proctored dosage exam. calculations final version key name: date: furosemide 50mg iv push now. available: furosemide how ... Using the following drug label, how many milliliters of Demerol would you give per dose? Answer _____0. Medication order: Heparin 25,000 units in 500 mL, infuse 4000 units/hr How many ... Dosage Calculations Nursing Comprehensive Quiz - Registered Nurse RN Dosage Calculations Nursing Practice Quiz Questions 1.) 27 mg= mcg * A. 270 mcg B. 27,000 mcg C. 0.027 mcg D. 37 mcg 2.) 6 tsp = ml * A. 5 mL B. 1.5 mL C. 30 mL D. 15 mL 3.) The doctor writes an order for a liquid oral medication. The order says to administer 15 mg by mouth every 4 hours as needed for sore throat. 4 Personality Disorders Nursing Care Plans - Nurseslabs Mar 18, 2022 · Personality is defined as the differences in the characteristic patterns of behaving, feeling and thinking of an individual.. A personality disorder is a type of mental illness in which a person’s personality traits have become rigid, inflexible, maladaptive and can hinder the person’s perception and association to situations and people.
Drug Calculations Involving Reading Drug Labels, Part 1 - YouTube Southwest Tech Math/Science Center 3.27K subscribers Practice performing drug dosage problems that require the use and understanding of drug labels to solve. Problem 1.) Determine the... PPIC Statewide Survey: Californians and Their Government Oct 27, 2022 · Key Findings. California voters have now received their mail ballots, and the November 8 general election has entered its final stage. Amid rising prices and economic uncertainty—as well as deep partisan divisions over social and political issues—Californians are processing a great deal of information to help them choose state constitutional officers and state legislators and to make ... Dosage Calculations: NCLEX-RN - Registered nursing Calculating Oral Medication Dosages Using Ratio and Proportion. Here is an example of how to calculate oral medication dosage using ratio and proportion: Doctor's order: 125 mg of medication once a day. Medication label: 1 tablet = 250 mg. How many tablets should be administered daily? PDF Drug dosage calculation handout for BSN completion 16. The provider orders 125mg of amoxicillin Q. 8 hrs. for a patient weighing 58 lbs. Calculate the daily dosage range recommended on the label and compare the daily dose ordered by the doctor. Does the provider order fall within the usual dosage range? 17. Aggrastat is ordered to infuse at 0.1 mcg/kg/min for a patient weighing 136 lbs. A ...
Dosage Calculation - Label Reading | Other - Quizizz Play this game to review Other. What is the dosage strength? Preview this quiz on Quizizz. Quiz. Dosage Calculation - Label Reading. DRAFT. 10th - University. Played 414 times. 72% average accuracy. Other, Life Skills. 6 months ago by. shelley_dinkens_86955. 3. Save. Edit. Edit. Dosage Calculation - Label Reading DRAFT. 6 months ago by. shelley ... Dosage Calculation Practice_Reading Labels.pdf - Dosage... Calculations (12-14) answers. 12) Number of of emtricitabine tablet required. Ordered dose = 200 mg. Available dose = 100 mg/tab. Number of tab required = 200/100 = 2 tablets. 13) ml of drug required. Volume (ml) = Desired dose/Dose in hand *Quantity. Here Desired dose = 600 mg. Dose in hand = 400 mg. Quantity = 1 ml. As per above formula dosage calculations worksheet Dosage calculations made easy for nursing students and nurses using dimensional analysis: comprehensive NCLEX review of drug calculations (nursing math).In t. Drug Dosage Calculations Drug Dosage Calculations Feb 05, 2012 · 1428344225, Pharmaceutical Calculations For Pharmacy Technicians: A Worktext, By Jahangir Moini, MD, MPH - ©Thomson. 72 ... How to Read a Medication Label Nursing Skill - YouTube Reading a medication label (drug label): medication administration (dosage and calculations) NCLEX pharmacology / new nurse review.Reading medication labels ...
ATI Dosage Calculations 3.0: Oral Medications - Quizlet Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like A nurse is preparing to administer methadone 2.5 mg PO every 8 hr. Available is methadone 5 mg tablets. How many tablets should the nurse administer per dose?, A nurse is preparing to administer quinapril 40 mg PO daily. Available is quinapril 20 mg tablets. How many tablets should the nurse administer daily?, A nurse is ...
Dosage Calculation Reading Drug Labels - StuDocu Dosage Calculation: Reading Drug Labels Chapter 11 Tarleton State University NURS 3310 Dr. Mary B. Winton Reading Drug Labels a. Brand/trade name b. Generic name c. Formulation d. Dosage strength e. Route f. Need prescription or Over -the-counter Reading Drug Labels and Reconstitution a. Generic name b. Brand/trade name c. Formulation d. Route e.
Drug Calculations Practice NCLEX Questions (100+ Items) - Nurseslabs Methods for Drug Dosage Calculations Standard Method The commonly used formula for calculating drug dosages. Where in: D = Desired dose or dose ordered by the primary care provider. H = dose on hand or dose on the label of bottle, vial, ampule. V = vehicle or the form in which the drug comes (i.e., tablet or liquid). STANDARD FORMULA
Dosage (Drug) Calculations Nursing Review- COMPREHENSIVE This is a comprehensive dosage calculation review for nursing students. In this review we will start by working basic metric conversions and then progress to solving more complex dosage calculations. You will learn how to work the following drug calculation problems: Conversions Oral Liquid Medications Capsules and Tablets IV Boluses
High Blood Pressure & Angina | NORVASC® (amlodipine besylate ... Indications NORVASC ® (amlodipine besylate) tablets are a prescription medicine to treat high blood pressure (hypertension), and certain types of chest pain (angina) and blocked arteries of the heart (coronary artery disease).
Lecture 3: Reading Medication Labels and Basic Dosage ... Since the ordered dosage is 0.75 g, we need to figure out how many tab it takes to make 0.75 g: _____tab=0.75 g. If we look closely, we notice that while the order is written in g, the label actually uses mg. We we need to convert g into mg if we want to be able to do any calculations that use the information given on the label.
Nursing Pharmacology: Dosage And Calculations Practice Test - RN speak The medication label reads "1,200,000 units per 2 mL." The nurse has determined that the dose prescribed is safe. The nurse administers how many milliliters per dose to the child? a. 0.8 mL b. 1.2 mL c. 1.4 mL d. 1.7 mL 19. Atropine sulfate, 0.6 mg intramuscularly, is prescribed for a child preoperatively.
CFR - Code of Federal Regulations Title 21 - Food and Drug ... Jul 20, 2022 · (d) Labels and other labeling materials for each different drug product, strength, dosage form, or quantity of contents shall be stored separately with suitable identification. Access to the storage area shall be limited to authorized personnel. (e) Obsolete and outdated labels, labeling, and other packaging materials shall be destroyed.
Dosage Calculator - How to Calculate Dosage? Let's say the appropriate dosage of the active substance is 2 mg/kg of body weight. Weigh yourself. Let's assume you weigh 80 kg. Multiply these two values to get the dose of medication in mg: 2 * 80 = 160 mg. You need to take 160 mg of active substance. What if your medication is liquid? Type the concentration into the proper box.
PDF Dosage Calculations Syllabus(1)new - Odessa College Chapter 6: Oral medication labels and dosage calculations (CO #1-5) The learner will: 1. Identify scored tablets, unscored tablets, and capsules. 2. Read drug labels to identify trade and generic names. 3. Locate dosage strengths and calculate average dosages. 4. Measure oral solutions using a medicine cup. Chapter 7: Safe medication administration
Lecture 3: Reading Medication Labels and Basic Dosage Calculations Every tenth of a cc(mL)is marked on the syringe, and every half cc(mL) is labeled; this means that any dosage we plan to measure using a 3 cc syringe should be rounded to the nearest tenth. Dosages between 1-3 mLshould always be measured in a 3 cc syringe.






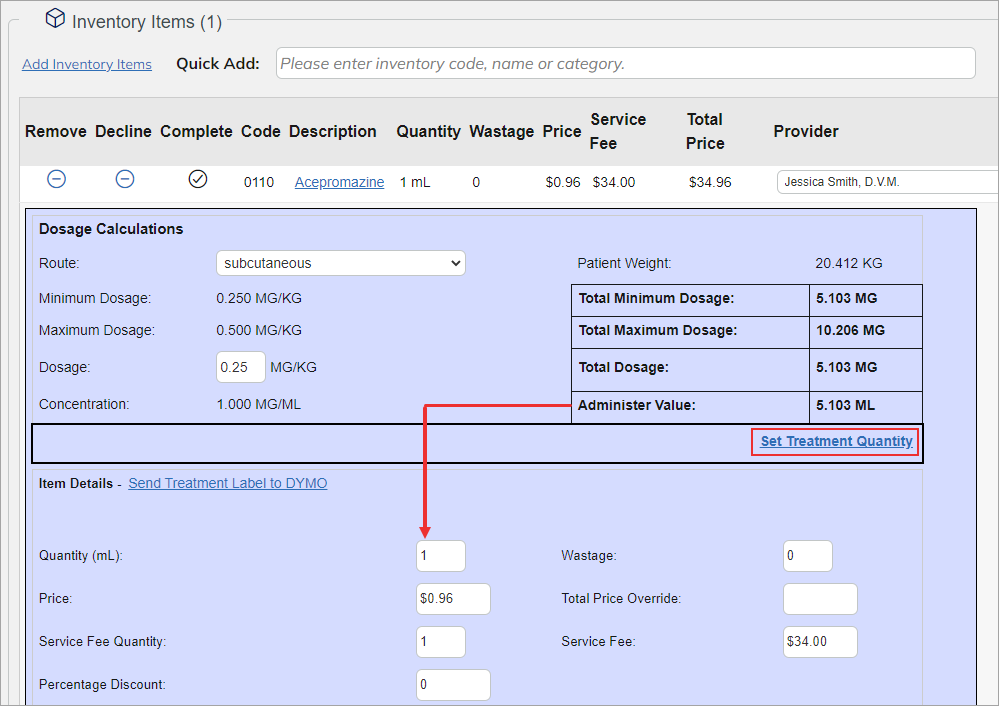


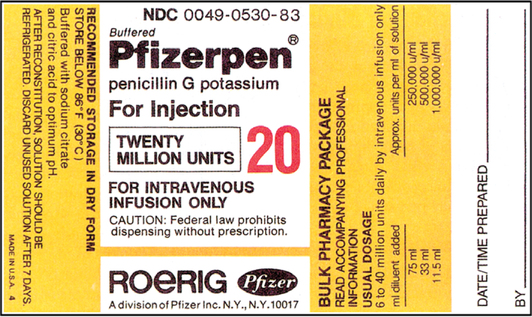
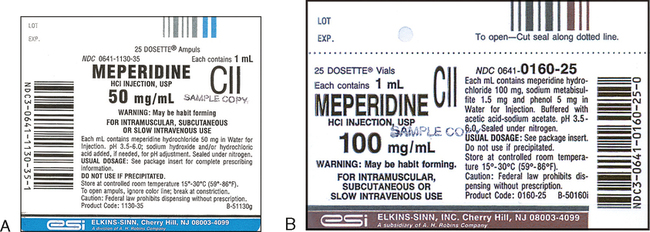
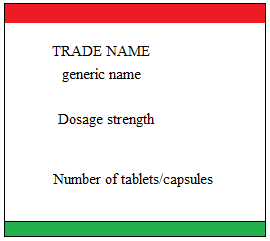


















Post a Comment for "39 dosage calculations with labels"